Introduction to Parrots: Overview and Key Characteristics
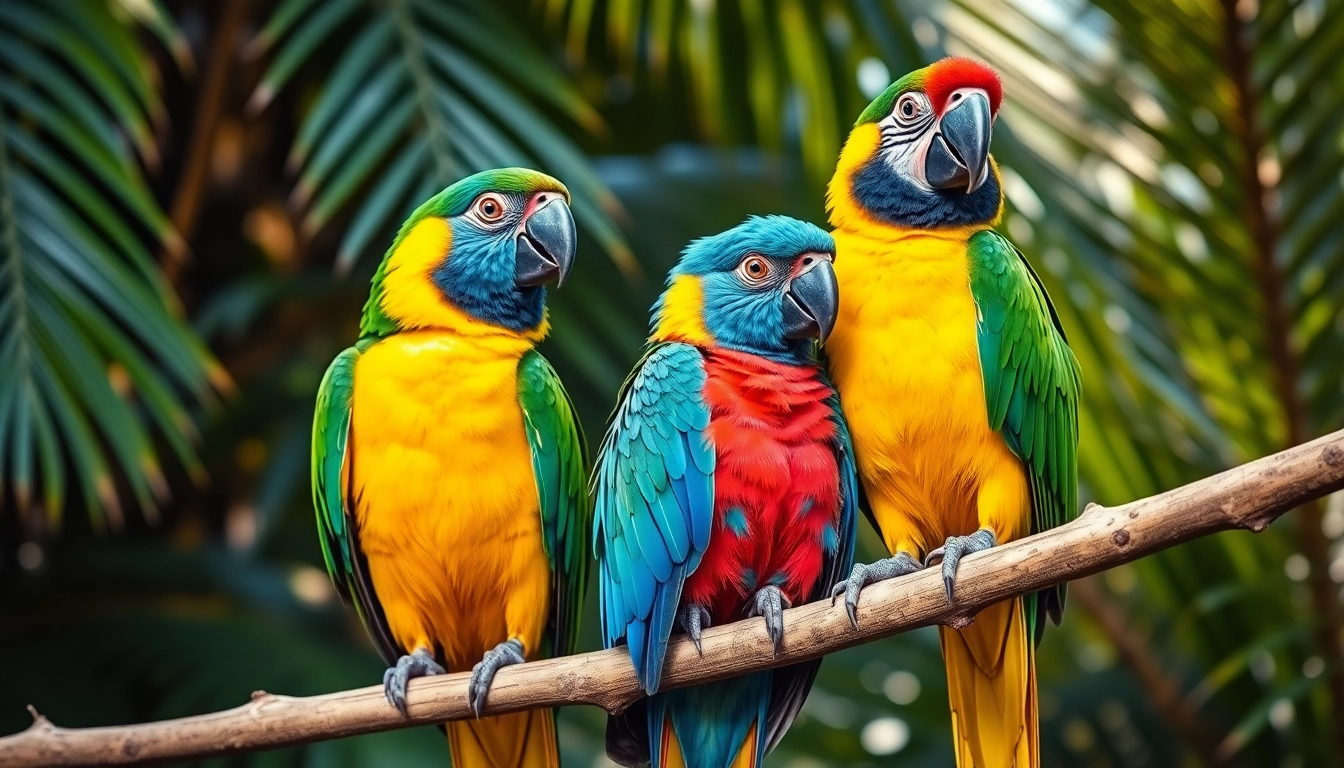
Parrots, known scientifically as Psittaciformes, represent one of the most vibrant and intelligent groups of birds on Earth. Their striking plumage, remarkable cognitive abilities, and vocal mimicry have fascinated humans for centuries. Found predominantly in tropical and subtropical regions, these birds have captivated bird enthusiasts, conservationists, and pet owners alike. Understanding parrots — their defining features, natural environments, and behavior — provides crucial insights for both appreciating these magnificent creatures and ensuring their well-being, whether in the wild or in captivity.
For a deeper exploration of these captivating birds, visit our comprehensive parrots guide designed to educate, inform, and inspire responsible interaction with these intelligent birds.
What Are Parrots? Defining Features and Classification
Defining Features of Parrots
Parrots are distinguished by their robust, curved beaks, which are perfectly adapted for their diet of nuts, fruits, and seeds. Their strong, clawed feet enable them to grasp objects with dexterity, a trait especially noticeable in species like the African grey. Their upright stance gives them a distinctive silhouette, and their vibrant plumage varies dramatically across species, ranging from vivid reds and blues to subtle greens and yellows.
Another characteristic that sets parrots apart is their exceptional intelligence. Many species use their beaks not only for feeding but also for manipulating objects, exploring their environment, and social interactions. Their cognitive abilities are comparable to those of primates, making them one of the most intelligent bird groups.
Taxonomy and Classification
Parrots belong to the order Psittaciformes, which encompasses roughly 410 species across four primary families. These families include Psittacidae (true parrots), Cacatuidae (cockatoos), Strigopidae (kākāpō and kakapo-like parrots), and Nestoridae (New Zealand parrots). The classification reflects their evolutionary adaptations, geographic distribution, and diverse traits. Despite their differences, all parrots share a common evolutionary lineage rooted in their specialized beak structure, zygodactyl feet (two toes facing forward, two backward), and their remarkable ability to mimic sounds.
Common Parrot Species and Their Unique Traits
Popular Parrot Species
- African Grey Parrot (Psittacus erithacus): Known for their high intelligence and exceptional speaking ability, African greys are medium-sized parrots with grey plumage and striking white eye rings. They can learn to mimic human speech with impressive clarity.
- Amazon Parrots: Recognized for their vibrant coloration and loud, playful calls, Amazon parrots thrive in the tropical forests of South America. Some popular species include the Yellow-headed Amazon and the Blue-fronted Amazon.
- Macaws (Hyacinth, Scarlet): Among the largest parrots, macaws are famous for their impressive size, brilliant coloration, and powerful beaks. Hyacinth macaws are known for their striking cobalt blue feathers and significant lifespan, reaching up to 50 years or more.
- Cockatoos: Distinct for their crest of feathers, cockatoos are highly social and intelligent. The Sulphur-crested cockatoo and the Umbrella cockatoo are examples of popular species kept as pets or found in the wild.
- Lovebirds: Small parrots with affectionate behaviors, lovebirds are known for their social nature and strong pair bonds, making them favorites among pet enthusiasts.
Traits That Make These Species Unique
Each species exhibits unique traits adapted to their natural habitats. For instance, macaws have powerful beaks designed for cracking hard nuts, while African greys excel in problem-solving and vocal learning. Understanding these particular traits assists in providing species-appropriate care and promotes their conservation needs.
Global Distribution and Natural Habitats of Parrots
Geographical Range
Parrots are primarily birds of the tropics and subtropical regions. Their natural range spans across Central and South America, Africa, Asia, and Australasia. Madagascar and New Zealand are notable exceptions, hosting unique, endemic species like the Kākāpō and Kakapo, which are critically endangered.
Interestingly, some parrots have adapted to regions outside their typical range. For example, the monk parakeet has established feral populations in parts of the United States, including Florida and New York, where they thrive in urban and suburban environments.
Natural Habitats
Parrots predominantly inhabit forests — rainforests, dry forests, and savannas — where they find ample food and nesting sites. They often nest in tree cavities, reaching up to high perches for safety and protection. Additionally, some species are adaptable to secondary forests and even urban settings, especially those with accessible food sources and nesting opportunities.
Their dependency on healthy ecosystems makes parrots sensitive indicators of environmental change. Loss of habitat due to deforestation threatens many species, underscoring the importance of conservation efforts to sustain their populations.
Parrot Care: How to Provide a Healthy Environment
Proper Housing and Feeding Guidelines for Parrots
Creating an environment that mimics their natural habitat is essential for pet parrots. A spacious cage with ample perches, toys, and enrichment items helps prevent boredom and promotes physical and mental health. The cage should be made of non-toxic materials, with bar spacing appropriate for the bird’s size to prevent injury.
Diet is equally critical: a balanced mixture of high-quality pellets, fresh fruits, vegetables, seeds, and nuts ensures nutritional adequacy. Fresh water must always be available. Avoiding harmful foods such as chocolate, caffeine, and avocados is vital, as these can be toxic to parrots.
Understanding Parrot Behavior and Needs
Parrots are highly social and intelligent creatures with complex behavioral needs. They thrive on interaction, mental stimulation, and a sense of security. Recognizing behaviors such as preening, vocalizing, and playing helps owners gauge their bird’s well-being. Behavioral issues often stem from boredom, neglect, or improper environment, which can be mitigated through enrichment activities and social bonding.
Training and Socialization Tips for Pet Parrots
Building a trusting relationship involves consistent, gentle handling and positive reinforcement. Start with short, daily interactions, gradually introducing new toys or commands. Parrots can be trained to step onto your hand, repeat words, or perform tricks, enhancing their mental stimulation and your bond. Socialization with other pets and humans reduces fear and promotes well-adjusted behavior.
Patience and understanding are key; every bird has a unique personality and comfort level, which should be respected during training and socialization.
Types of Parrots: From Popular Pets to Wild Species
Popular Parrot Breeds and Their Care Requirements
Choosing the right parrot depends on your lifestyle, experience, and commitment. For example, African grey parrots require mental stimulation and social interaction, whereas smaller species like lovebirds are more manageable for beginners. Understanding each breed’s specific needs for diet, cage size, socialization, and enrichment is crucial for their health and happiness.
Wild Parrot Species and Their Conservation Status
Many wild parrot species face threats from habitat destruction, illegal pet trade, and climate change. The Hyacinth macaw, for example, is classified as vulnerable due to habitat loss and poaching. The New Zealand’s kakapo, a flightless nocturnal parrot, is critically endangered with fewer than 250 individuals remaining, highlighting urgent conservation needs.
Choosing the Right Parrot for Your Lifestyle
Potential owners should consider factors like space, time commitment, noise levels, and experience. Larger parrots tend to be more intelligent and long-lived but require more social interaction and mental stimulation. Smaller parrots may be suitable for apartments but still demand daily care and enrichment. Responsible selection promotes the well-being of the bird and reduces the likelihood of relinquishment or neglect.
Fun Facts and Interesting Insights about Parrots
Long Lifespans and Intelligence of Parrots
Parrots are renowned for their impressive lifespans, with some species like the Kākāpō living up to 60 years. Their cognitive abilities are equally extraordinary; they can solve puzzles, learn to mimic human speech, and even demonstrate problem-solving skills akin to primates, making them one of the most intelligent avian groups.
Parrots’ Ability to Mimic Human Speech and Bonding Behaviors
Birds like the African grey have an uncanny ability to imitate a wide range of sounds, including human speech, often forming deep bonds with their owners. Bonding behaviors include preening, vocal mimicry, and seeking physical closeness, reflecting a high level of social intelligence and emotional connection.
Uncommon Parrot Facts That Will Surprise You
- Parrots eat with their feet, much like primates use their hands, enabling precise manipulation of food items.
- They are among few animals capable of understanding and responding to human gestures or commands, showcasing their complex cognition.
- Many parrots are monogamous, forming lifelong pair bonds during their breeding season.
- The Hyacinth macaw’s powerful beak can crack hard nuts and is strong enough to disable a human finger.
- Some species, like the Monk parakeet, are adaptable urban dwellers, thriving in city environments worldwide.
Conservation and Ethical Considerations for Parrot Enthusiasts
Threats Facing Wild Parrots and Protection Initiatives
The decline of wild parrot populations is driven by habitat destruction, illegal trapping, and the pet trade. Logging and land conversion eliminate nesting sites, while poaching depletes wild stocks. Conservation organizations like the World Parrot Trust work tirelessly to combat these threats through habitat protection, education, and breeding programs.
How to Support Parrot Conservation Efforts
Supporting reputable conservation organizations, advocating against illegal trade, and participating in habitat restoration projects all contribute to safeguarding wild parrot populations. Educating others about the importance of sustainable practices and responsible ownership helps reduce demand for wild-caught birds and promotes ethical breeding.
Responsible Ownership and Ethical Breeding Practices
Prospective owners should seek parrots from ethical breeders who prioritize health, genetic diversity, and animal welfare. Avoiding illegal or unregulated trade prevents contributing to population declines. Commitment to proper care, socialization, and lifelong attention is essential for the ethical stewardship of these extraordinary birds.